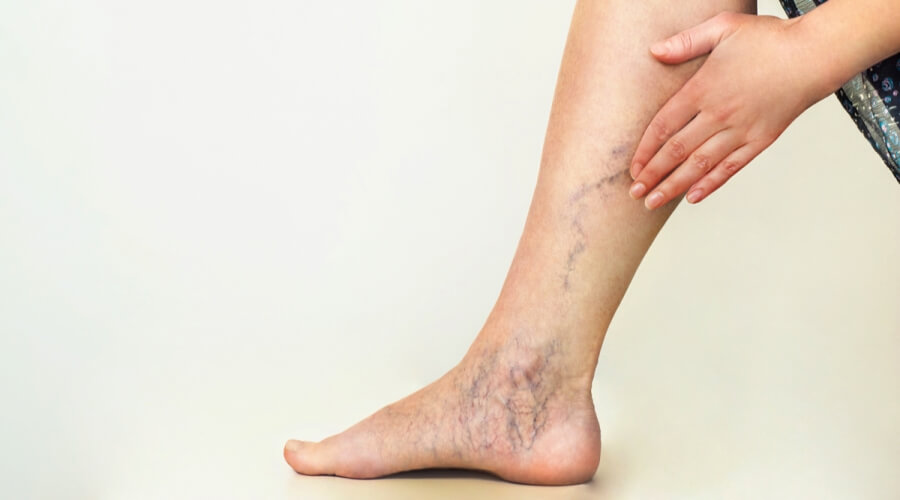
Varicose veins are a common condition affecting blood vessels, especially in the legs, where the veins appear enlarged, twisted, and protruding under the skin with a blue or purple color. This condition is not just a cosmetic issue but can also cause significant pain and discomfort for many sufferers. In this article, we will review in detail the causes of varicose veins, their symptoms, risk factors, potential complications, and the latest treatment methods available to deal with this troublesome health problem.
What are Varicose Veins?
Varicose veins are dilated and enlarged veins that usually appear in the legs and feet, where the small valves inside the veins fail to prevent blood from flowing backward, leading to blood pooling and vein enlargement. These veins appear dark blue or purple and are twisted and swollen like ropes under the skin. Varicose veins affect about 25% of adults and are more common in women than men.
Main Causes of Varicose Veins
Weakened Vein Valves
The primary cause of varicose veins is the failure of the small valves inside the veins to function properly. Normally, these valves prevent blood from flowing backward as it moves towards the heart. When these valves weaken or become damaged, blood leaks backward and pools in the vein, causing it to enlarge and varicose veins to appear.
Hormonal Factors
Female hormones play a significant role in the development of varicose veins, as estrogen and progesterone cause the walls of the veins to relax, making the valves more prone to leakage. This explains why varicose veins are more prevalent among women, especially during pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause.
Aging
With age, veins lose their elasticity, and the valves become weaker, increasing the risk of developing varicose veins. Varicose veins often appear between the ages of 30 and 70, and the risk increases after the age of 40.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy is a major factor in the development of varicose veins in women, as the blood volume in the body increases to support the fetus, putting pressure on the veins. Hormonal changes during pregnancy also cause the walls of the veins to relax. Additionally, the expanding uterus presses on the veins in the pelvic area, hindering the return of blood to the heart.
Prolonged Standing or Sitting
Jobs that require prolonged standing or sitting without movement increase the risk of varicose veins because they impede blood circulation and increase pressure on the leg veins.
Obesity and Excess Weight
Excess weight puts extra pressure on the veins, especially in the legs, increasing the risk of them stretching and their valves weakening.
Genetic Factors
If there is a family history of varicose veins, the risk of developing them increases significantly. Studies indicate that genetic predisposition plays an important role in the appearance of varicose veins.
Other Causes
Rare causes of varicose veins include: previous blood clots, pelvic tumors, or blood vessel malformations.
Symptoms of Varicose Veins
Varicose veins do not cause pain in all cases, but they may be accompanied by several bothersome symptoms, including:
- Visible veins: Enlarged, twisted, and protruding veins under the skin, blue or purple in color.
- Pain and heaviness in the legs: Especially after prolonged standing or sitting.
- Swelling of the ankles and feet: Due to fluid retention.
- Itching and burning: Around the affected veins.
- Muscle cramps: Especially at night.
- Skin discoloration: The skin around the varicose veins becomes dark or changes color.
- Feeling of tired legs: Especially at the end of the day.
- Appearance of spider veins: Small red or blue blood vessels that resemble a spider web.
Complications of Varicose Veins
If varicose veins are left untreated, they may lead to several serious complications, including:
- Superficial thrombophlebitis: A painful inflammation of the vein that may be accompanied by a blood clot.
- Skin ulcers: Usually appear near the ankles due to poor blood circulation.
- Bleeding: Veins close to the skin may rupture and cause bleeding.
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT): In rare cases, varicose veins may lead to deep vein thrombosis, a serious condition requiring immediate treatment.
- Lipodermatosclerosis: Where the fat under the skin becomes hard, leading to skin contraction.
- Venous eczema: A skin condition causing itching and redness.
Treatment Methods for Varicose Veins
Treatment for varicose veins depends on the severity of the condition and the accompanying symptoms. Treatment options include:
1. Lifestyle Changes
- Regular exercise: Especially walking and swimming to improve blood circulation.
- Elevating the legs: When sitting or lying down to facilitate blood return to the heart.
- Avoiding prolonged standing or sitting: With regular changes in position.
- Losing excess weight: To reduce pressure on the veins.
- Avoiding tight clothing: Especially around the waist and thighs.
- Avoiding high heels: As they impede blood circulation in the legs.
2. Compression Stockings
Compression stockings are the first step in treating varicose veins, as they compress the legs to help blood flow towards the heart more efficiently. These stockings are tightest at the ankle and gradually become looser as they go up the leg. It is recommended to wear them throughout the day and remove them at night.
3. Sclerotherapy
In this procedure, a chemical solution is injected into the affected vein, causing it to irritate and close. Over time, the vein turns into scar tissue and disappears. This treatment is used for small to medium-sized varicose veins. There are two types of sclerotherapy:
- Liquid sclerotherapy: For mild cases.
- Foam sclerotherapy: For larger varicose veins.
4. Laser Treatment
This procedure uses strong laser beams to heat and close the affected vein. Laser treatment is done through the skin without the need for surgical incisions and is suitable for small varicose veins and spider veins.
5. Radiofrequency Ablation
A small catheter is inserted into the affected vein, and radio waves are then used to heat and close the vein. This procedure is considered less invasive than traditional surgery and is performed under local anesthesia.
6. Traditional Surgery
In severe cases, the doctor may resort to surgery to remove large varicose veins. Surgical options include:
- Vein ligation and stripping: Where the affected vein is tied off and removed through small incisions.
- Endoscopic vein surgery: Used in advanced cases accompanied by skin ulcers.
7. Adhesive Injection Therapy
This is a modern procedure that uses a special medical adhesive to close the affected vein without the need for heat or chemical injections.
Prevention of Varicose Veins
Although varicose veins cannot be completely prevented, especially if there are genetic factors, some measures may reduce the risk of developing them or prevent the condition from worsening:
- Maintaining a healthy weight: To reduce pressure on the veins.
- Regular exercise: To improve blood circulation and strengthen leg muscles.
- Avoiding prolonged sitting or standing: With regular changes in position and walking every hour.
- Elevating the legs: When sitting or sleeping to facilitate blood return to the heart.
- Wearing comfortable clothing: And avoiding tight clothing around the waist and thighs.
- Avoiding high heels: And choosing comfortable shoes with low heels.
- Eating a healthy diet: Rich in fiber and low in salt to prevent fluid retention.
When to See a Doctor?
It is advisable to see a doctor in the following cases:
- If varicose veins cause severe pain or discomfort.
- When skin ulcers appear near the ankles.
- In case of bleeding from the affected veins.
- If the leg becomes swollen, red, or hot, which may indicate a blood clot.
- When noticing skin discoloration around the varicose veins.
- If symptoms do not improve with self-care.
Conclusion
Varicose veins are a common condition affecting the veins, especially in the legs, and result from weakened vein valves and other factors such as aging, pregnancy, prolonged standing, and genetic factors. Although varicose veins may not cause pain in all cases, they can lead to serious complications if left untreated. Treatment options include lifestyle changes, compression stockings, sclerotherapy, laser, and surgery in severe cases. Early prevention and self-care can reduce the risk of developing varicose veins or prevent them from worsening. If you experience bothersome symptoms or complications, it is important to consult a doctor to assess the condition and choose the appropriate treatment.